This manual provides a comprehensive introduction to microbiology lab techniques, procedures, and essential safety protocols. It includes detailed exercises and an answer key to guide students through practical applications, ensuring mastery of foundational microbiology skills.
Overview of the Lab Manual
This lab manual is a comprehensive resource for students, covering microbiological applications, laboratory procedures, media preparation, and safety protocols. It includes exercises, detailed solutions, and step-by-step explanations to aid in mastering microbiology techniques. The manual serves as a practical guide for both classroom and lab settings, ensuring students gain hands-on experience and theoretical knowledge. Regularly updated, it provides the latest advancements in microbiology, making it an indispensable tool for learning.
Importance of the Answer Key in Microbiology Studies
The answer key is an essential tool for students, providing clear solutions to lab exercises and reinforcing understanding of microbiological concepts. It helps verify results, correct errors, and build confidence in performing techniques like gram staining and bacterial identification. With detailed explanations, it serves as a self-assessment resource, ensuring students grasp critical lab skills and apply them effectively in real-world scenarios.
Key Laboratory Techniques in Microbiology
Mastering techniques like streak plating, gram staining, and bacterial identification is crucial. The answer key guides students through these procedures, ensuring accurate results and skill development.
Streak Plate Method
The streak plate method is a fundamental technique for isolating pure bacterial cultures. It involves spreading bacteria across an agar plate in a pattern of parallel lines or streaks. The answer key provides step-by-step guidance, ensuring students understand how to properly inoculate and incubate plates. This method helps in obtaining isolated colonies, essential for bacterial identification. The answer key also highlights common errors, such as improper sterilization or excessive inoculum, to optimize results and maintain contamination control.
Gram Staining Procedure
The Gram staining procedure is a critical differential staining method used to classify bacteria into Gram-positive and Gram-negative groups. It involves applying crystal violet, iodine, alcohol, and safranin dyes. The answer key provides detailed steps, emphasizing proper smear preparation, staining times, and decolorization. This technique helps identify bacterial cell wall structures, with Gram-positive bacteria appearing purple and Gram-negative bacteria pink under a microscope. The guide ensures accurate results by addressing common errors, such as over-decolorization or insufficient heat fixation.
Bacterial Identification Techniques
Bacterial identification techniques combine morphological, biochemical, and molecular methods to classify microorganisms; The answer key provides step-by-step guidance for performing tests like Gram staining, catalase, and oxidase assays. It also covers the use of selective and differential media to distinguish bacterial species. These techniques are essential for accurate identification, enabling students to correlate phenotypic and genotypic characteristics. The manual emphasizes proper test interpretations to ensure reliable and reproducible results in microbiology studies;

Microbiology Lab Safety Protocols
Microbiology lab safety protocols emphasize handling biological hazards, proper use of PPE, and waste disposal. The answer key provides guidelines for biosafety levels and emergency procedures.
Handling Biological Hazards
Handling biological hazards in a microbiology lab requires strict adherence to biosafety protocols. Biological agents, such as bacteria and viruses, pose risks of infection or contamination. Proper containment, such as using biosafety cabinets, and personal protective equipment (PPE) are essential. The answer key provides detailed procedures for safe handling, storage, and disposal of biological materials. Decontamination methods, like autoclaving, are emphasized to minimize risks. Understanding biosafety levels (BSL-1 to BSL-4) is critical for appropriate handling practices.
Proper Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Proper use of PPE is vital in microbiology labs to prevent exposure to biological hazards. Lab coats, gloves, goggles, and face shields are essential to protect skin and mucous membranes. The answer key outlines correct PPE donning and doffing procedures to avoid contamination. Disposable gloves must be worn when handling cultures or hazardous materials, and lab coats should be closed and buttoned. Ensuring PPE is used correctly minimizes risks of infection and ensures a safe working environment for all personnel.
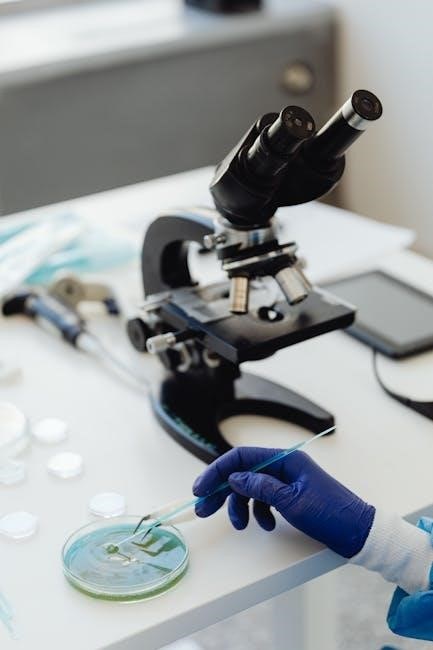

Preparation of Culture Media
Microbiology lab manuals detail culture media preparation, including agar plates and liquid media, to support microbial growth. Proper sterilization ensures contamination-free environments for experiments and analysis;
Types of Culture Media
Culture media in microbiology are categorized into solid, liquid, and semi-solid types. Solid media, like agar plates, support bacterial colonies for isolation. Liquid media, such as broth, enable microbial growth in suspension. Selective media inhibit certain organisms, while differential media help identify bacteria based on metabolic traits. Enriched media enhance the growth of specific microorganisms. Proper preparation and sterilization of these media are critical for accurate experimental results and contamination-free environments in laboratory settings.
STERILIZATION Techniques
Sterilization is a critical process in microbiology to eliminate all forms of microbial life. Common methods include autoclaving, which uses high-pressure steam, and ethylene oxide for heat-sensitive materials. UV light is used for surface sterilization, while filtration is applied to liquids. Proper sterilization ensures contamination-free experiments and maintains the integrity of cultures. Each technique requires specific protocols to validate effectiveness, making it essential for accurate laboratory outcomes and safety.
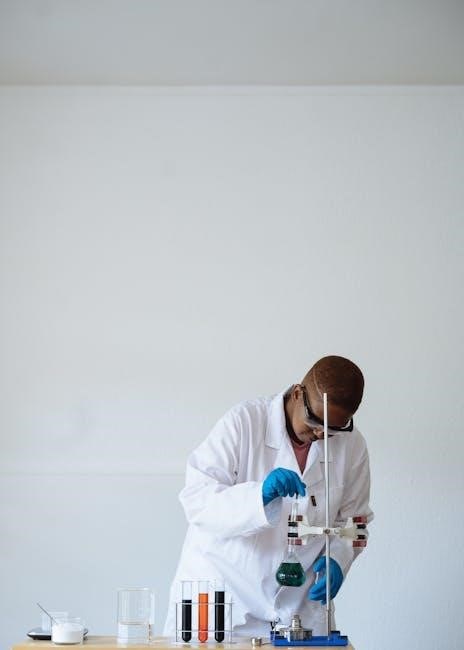

Microscopy in Microbiology Labs
Microscopes are essential tools for studying microorganisms, enabling detailed observation of their structure. Proper techniques, including staining and magnification, are critical for accurate identification and analysis in labs.
Usage and Maintenance of Microscopes
Proper microscope handling is crucial for accurate observations. Clean lenses with soft cloths and avoid touching glass surfaces. Focus using low magnification first, then switch to higher powers. Regularly maintain and calibrate microscopes to ensure optimal performance. Store instruments in dry, cool places to prevent damage. Follow manufacturer guidelines for maintenance to extend the microscope’s lifespan and reliability in microbiology studies.
Preparation of Slides for Observation
Slide preparation involves placing a biological sample on a clean glass slide. Apply a small drop of water or stain, then spread the sample evenly using a sterile loop or swab. For heat-fixed smears, pass the slide through a flame to kill bacteria and adhere them to the slide. Stain as required for differential staining techniques, such as Gram staining, to enhance visibility under a microscope. Clean slides thoroughly after use to prevent contamination.
Microbial Identification and Classification
Microbial identification involves techniques like differential staining and biochemical tests to classify bacteria. The answer key provides step-by-step solutions for accurate identification and classification processes.
Differential Staining Methods
Differential staining methods, like Gram and Acid-Fast staining, help identify bacteria by highlighting structural differences. Gram staining distinguishes Gram-positive (purple) and Gram-negative (pink) bacteria, while Acid-Fast staining identifies bacteria with waxy cell walls; These techniques are essential for bacterial classification and diagnosis. The answer key provides detailed protocols and expected results, ensuring students master these critical identification skills through step-by-step guidance and troubleshooting tips.
Biochemical Tests for Bacterial Identification
Biochemical tests are crucial for identifying bacteria based on their metabolic capabilities. Tests like the catalase, oxidase, and urease tests reveal enzyme activity. The answer key provides expected outcomes, enabling students to interpret results accurately. These tests, coupled with selective media, help differentiate bacteria into specific genera and species, ensuring precise identification and understanding of microbial physiology through structured lab exercises and explanations.

Common Microbiology Lab Experiments
Experiments include antimicrobial susceptibility testing, environmental sampling, and bacterial identification. The answer key provides solutions to exercises, ensuring accurate results interpretation and practical skill mastery.
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing determines the effectiveness of antibiotics against specific bacterial strains. Using methods like disk diffusion, students observe inhibition zones to categorize bacteria as susceptible, resistant, or intermediate. The answer key provides expected results, helping students interpret data accurately. This exercise enhances understanding of antimicrobial resistance and informs clinical treatment decisions. Proper techniques ensure reliable outcomes, aligning with standardized protocols for precise results analysis and reporting.
Environmental Sampling and Analysis
Environmental sampling involves collecting and testing samples from water, soil, or air to identify microbial communities. Techniques like swabbing or filtration are used to isolate microorganisms. The answer key provides reference data for identifying species and interpreting results. This exercise teaches students to assess microbial diversity, detect pathogens, and evaluate environmental health risks. Accurate analysis ensures reliable conclusions, enhancing understanding of ecological microbial interactions and human impact on ecosystems.
Lab Reports and Data Interpretation
Lab reports require clear, concise documentation of methods, results, and conclusions. The answer key provides templates and examples to ensure accurate data interpretation and proper formatting.
Writing Effective Lab Reports
Writing effective lab reports involves clear communication of objectives, methods, results, and conclusions. The answer key provides templates and examples to ensure accuracy and proper formatting. It guides students in presenting data, interpreting results, and drawing logical conclusions. Proper structure, including introduction, materials, procedures, and discussion, is emphasized. The manual also highlights the importance of professionalism and clarity in scientific writing, enabling students to produce high-quality reports that reflect their understanding of microbiology concepts and techniques.
Interpreting Microbiology Lab Results
Interpreting lab results requires understanding data in the context of experimental objectives; The answer key provides clear guidelines for analyzing microbiological data, such as identifying bacteria through Gram staining or biochemical tests. It helps students determine the significance of results, including antimicrobial susceptibility or environmental microbial communities. Proper interpretation ensures accurate conclusions, linking lab findings to real-world applications and further studies, enhancing both critical thinking and practical skills in microbiology.
Case Studies in Microbiology

Case studies provide real-world applications of microbiology techniques, allowing students to analyze microbial communities and their interactions. The answer key offers insights into practical lab scenarios and their relevance to microbiological principles.
Real-World Applications of Lab Techniques
Lab techniques in microbiology are essential for addressing real-world challenges, such as environmental sampling, disease diagnosis, and food safety. The answer key provides insights into applying methods like gram staining and bacterial identification to real scenarios, ensuring accurate and reliable results. These applications highlight the importance of microbiological practices in public health, agriculture, and industrial processes, preparing students for practical challenges in the field.
Analyzing Microbial Communities in Different Environments
Microbial communities vary across environments, from soil to human bodies. Lab techniques, such as culturing and staining, help identify and characterize these microbes. The answer key guides students in analyzing environmental samples, understanding microbial diversity, and linking it to ecosystem function. This knowledge aids in addressing public health issues, agricultural productivity, and environmental conservation, showcasing the practical importance of microbiological studies in real-world scenarios.
Mastery of microbiology lab techniques is essential for understanding microbial interactions and their applications. The answer key serves as a vital resource, ensuring accuracy and confidence in laboratory outcomes.
Final Thoughts on Mastering Microbiology Lab Techniques
Mastering microbiology lab techniques requires dedication and practice. The answer key in the lab manual is a crucial tool for verifying results and understanding procedures. It helps students identify errors and improve their skills. Regular use of the manual ensures proficiency in methods like streak plating and Gram staining. By following guidelines and safety protocols, students gain confidence in handling biological samples and conducting accurate experiments. This foundational knowledge is essential for advancing in microbiology and related fields.

No Responses